Overview of DS1307 RTC Module
- Real Time Clock (RTC) is used for monitoring time and maintaining a calendar.
- In order to use an RTC, we need to first program it with the current date and time. Once this is done, the RTC registers can be read at any time to know the time and date.
- DS1307 is an RTC which works on the I2C protocol. Data from various registers can be read by accessing their addresses for reading using I2C communication.
RTC Module Details:
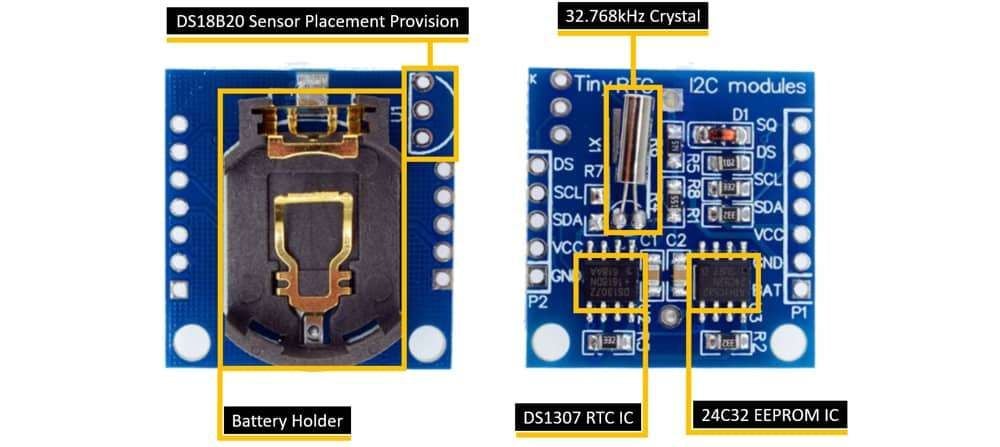
DS1307 RTC IC: DS1307 is 8-Pin main RTC (Real Time Clock) chip which provide real time clock and calendar, on the I2C communication protocol. It is a very low power chip which consumes less than 500nA current.
This chip provides time in second, minute, and hour format and calendar in date, month, and year format. The time supports both 24Hrs as well as 12Hrs AM/PM indicator.
24C32 EEPROM IC: This module come with 32 bytes Atmel 24C32 EEPROM chip which is used to save the settings or time and date. It is also operating on I2C communication bus.
32.768kHz Crystal: In this module have one crystal oscillator which provides the 32.768kHz clock frequency to the DS1307 RTC chip.
Battery Holder: This is the CR2032 type battery holder. The CR2032 is a 3V lithium coin cell battery which gives uninterrupted backup supply to the DS1307 RTC chip.
DS18B20 Sensor Provision: This module provides the provision to solder and use the DS18B20 temperature sensor. It is not come with pre-soldered. If you want then solder the trough hole package and get the temperature on the DS pin of this module.
RTC Module Pinout:
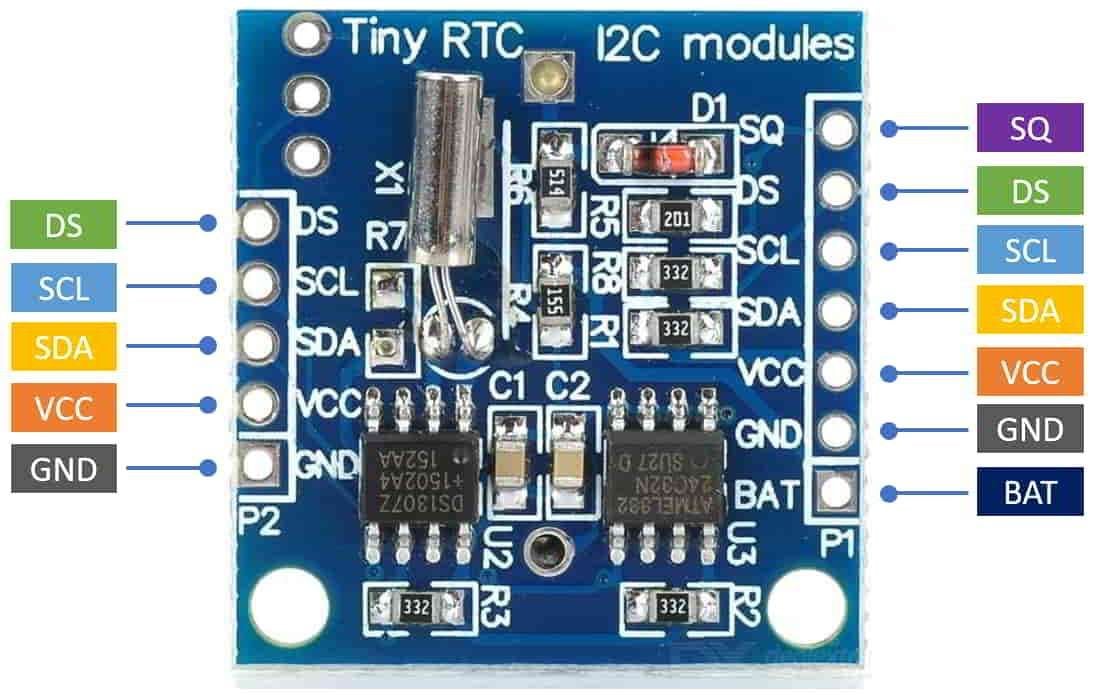
DS1307 RTC Module Pin Specifications:
VCC: It is the input supply voltage pin of the module which requires the DC voltage in the range of 3.3V to 5.5V.
GND: It is a supply ground pin.
SDA: This is a data pin of the I2C bus
SCL: This is a clock pin of the I2C bus
DS: This pin is used to read the temperature from the DS1307 temperature sensor if it is installed on the RTC module.
SQ: This pin produces a square-wave output of frequency 1 Hz, 4 kHz, 8 kHz, or 32 kHz and depends on programming logic.
BAT: This is the battery backup pin that requires a 3V input supply to keep maintain accurate timekeeping when the main power to the device is interrupted.
For information on DS1307 and how to use it, refer the topic RTC (Real Time Clock ) DS1307 Module in the sensors and modules section.
DS1307 RTC Hardware Connection with ESP32
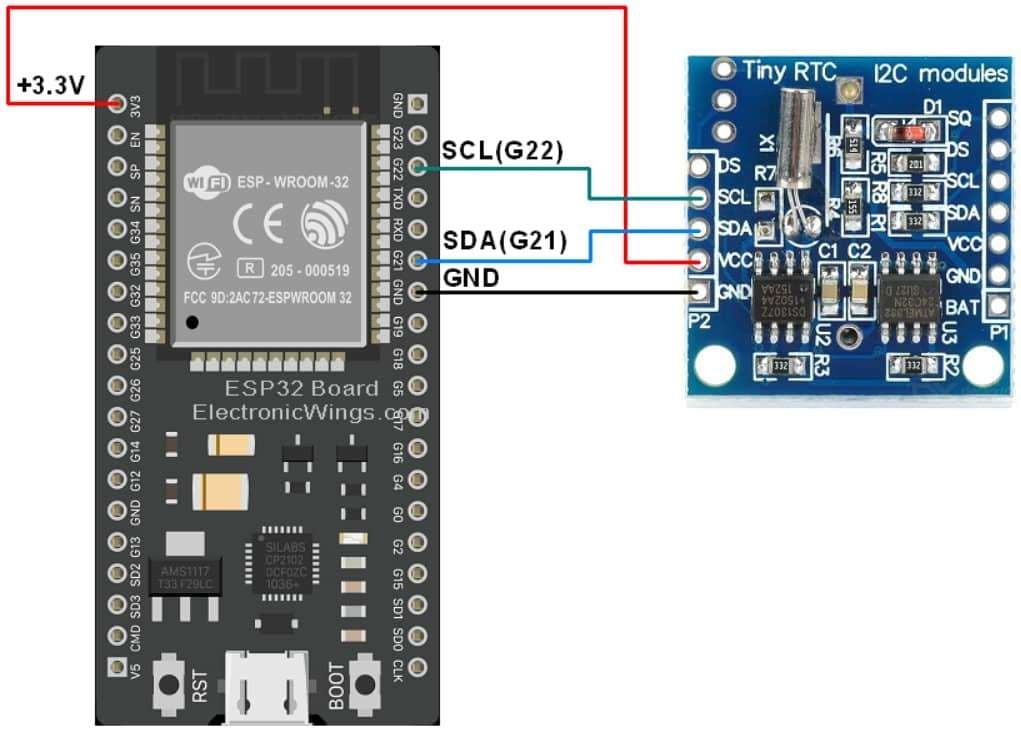
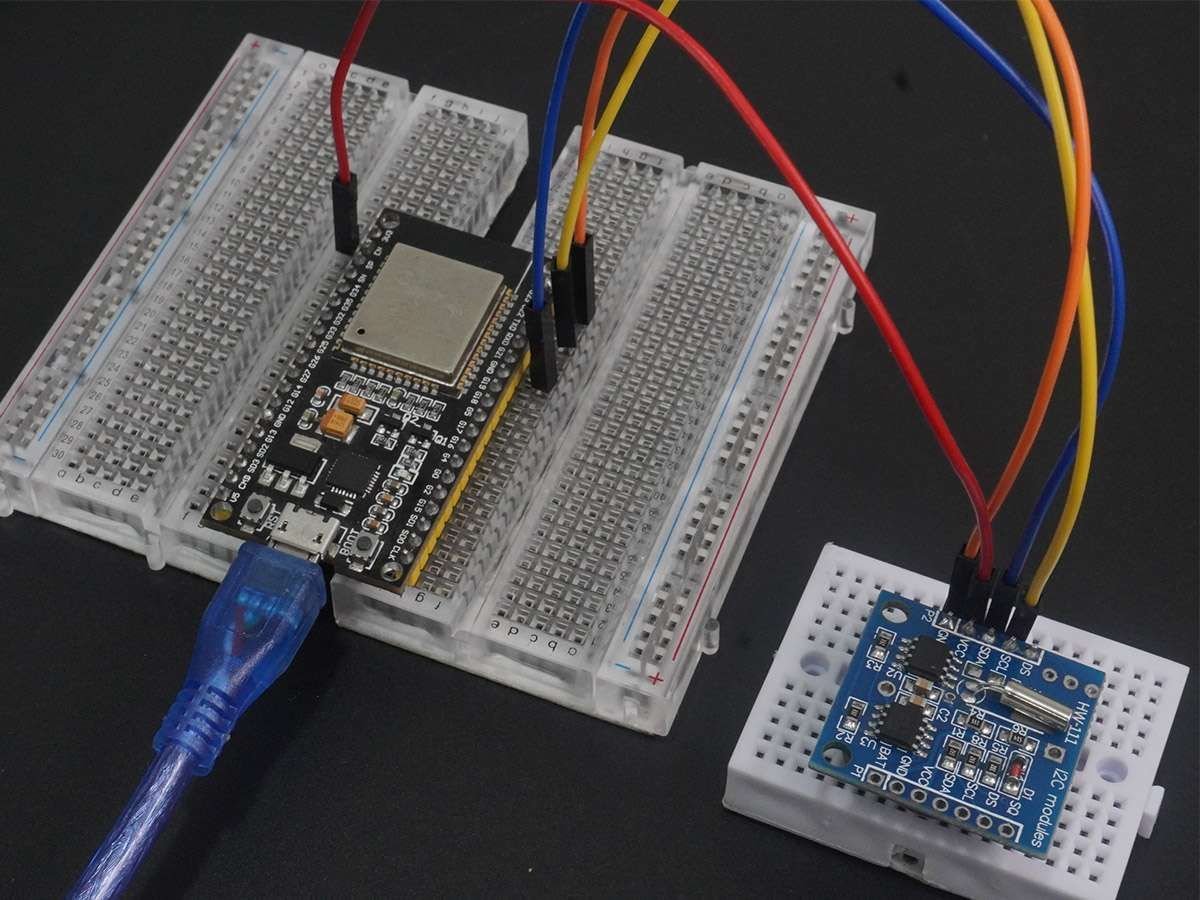
Set the current time in the RTC DS1307 using ESP32
Now let’s interface the DS1307 RTC to ESP32 and program the ESP32 to feed/Set the RTC with the current date and time using ESP32 and Arduino IDE.
Then we will read the date and time from the RTC in the next example.
Here, we will be using the DS1307 library by Watterott from GitHub.
Download this library from here.
Extract the library and add the folder named DS1307 to the library’s folder path of Arduino IDE.
For information about how to add a custom library to the Arduino IDE and use examples from it, refer Adding Library To Arduino IDE in the Basics section.
Once the library has been added to the Arduino IDE, open the IDE and copy the below code and paste it into your Arduino IDE.
Before uploading the code make sure you have set your current date and time in the code as follows.
uint8_t set_Sec = 0; /* Set the Seconds */
uint8_t set_Minute = 47; /* Set the Minutes */
uint8_t set_Hour = 3; /* Set the Hours */
uint8_t set_Day = 13; /* Set the Day */
uint8_t set_Month = 05; /* Set the Month */
uint16_t set_Year = 2022; /* Set the Year */
Code for Set time and Date in DS1307 RTC using ESP32
#include <DS1307.h>
uint8_t set_Sec = 0; /* Set the Seconds */
uint8_t set_Minute = 47; /* Set the Minutes */
uint8_t set_Hour = 3; /* Set the Hours */
uint8_t set_Day = 13; /* Set the Day */
uint8_t set_Month = 05; /* Set the Month */
uint16_t set_Year = 2022; /* Set the Year */
uint8_t sec, minute, hour, day, month;
uint16_t year;
DS1307 rtc;
void setup(void){
Serial.begin(115200); /*Set the baudrate to 115200*/
rtc.begin();
/*03:47:00 13.05.2022 //sec, min, hour, day, month, year*/
rtc.set(set_Sec, set_Minute, set_Hour, set_Day, set_Month, set_Year);
rtc.stop(); /*stop/pause RTC*/
rtc.start(); /*start RTC*/
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
Serial.print("You have set: ");
Serial.print("\nTime: ");
Serial.print(set_Hour, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(set_Minute, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(set_Sec, DEC);
Serial.print("\nDate: ");
Serial.print(set_Day, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(set_Month, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(set_Year, DEC);
Serial.println("");
}
void loop(void){}
- Now upload the code on your ESP32 board. (while uploading the code make sure your ESP32 board is in the boot mode.)
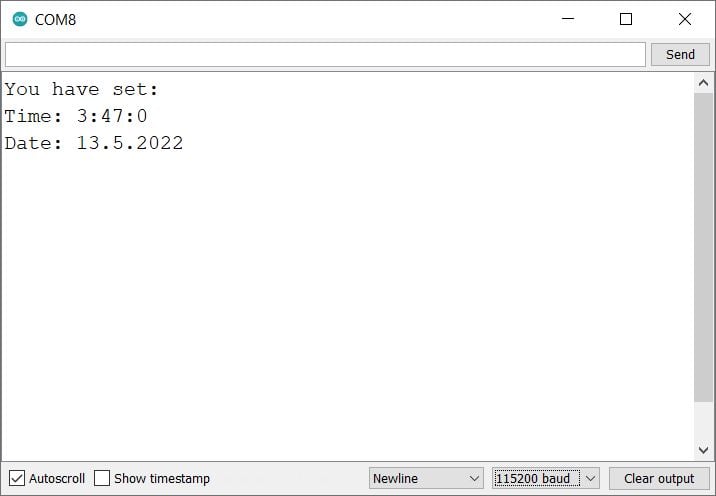
- Now open the serial monitor and reset the ESP32 you will get on a serial monitor as shown in the below image.
ESP32 serial monitor output for DS1307 RTC
Important functions
To ensures the connection between DS1307 and ESP32 using begin() function
rtc.begin();set() function is used to set the current time and date into DS1307 RTC IC.
rtc.set(uint8_t sec, uint8_t min, uint8_t hour, uint8_t day, uint8_t month, uint16_t year)This function is used to start I2C communication with DS1307. It fetches the SEC and CH byte from the DS1307 Timekeeper registers.
rtc.start()To get the time and date stored in DS1307 using get() function
rtc.get(uint8_t *sec, uint8_t *min, uint8_t *hour, uint8_t *day, uint8_t *month, uint16_t *year)The stop() function is used to stop I2C communication with DS1307.
rtc.stop();
Read the Time and Date using RTC DS1307 and ESP32
Now let’s read the date and time which we have set on the DS1307 RTC chip and display it on the serial monitor using ESP32 and Arduino IDE.
Sketch for DS1307 RTC Serial Monitor using ESP32
#include <DS1307.h>
uint8_t sec, minute, hour, day, month;
uint16_t year;
DS1307 rtc;
void setup(void){
Serial.begin(115200); /*Set the baudrate to 115200*/
rtc.begin();
rtc.start(); /*start RTC*/
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
}
void loop(void){
/*get time from RTC*/
rtc.get(&sec, &minute, &hour, &day, &month, &year);
/*serial output*/
Serial.print("\nTime: ");
Serial.print(hour, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minute, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(sec, DEC);
Serial.print("\nDate: ");
Serial.print(day, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(month, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(year, DEC);
Serial.println("");
/*wait a second*/
delay(1000);
}
- Now upload the code. (While uploading the code make sure your ESP32 board is in the boot mode.)
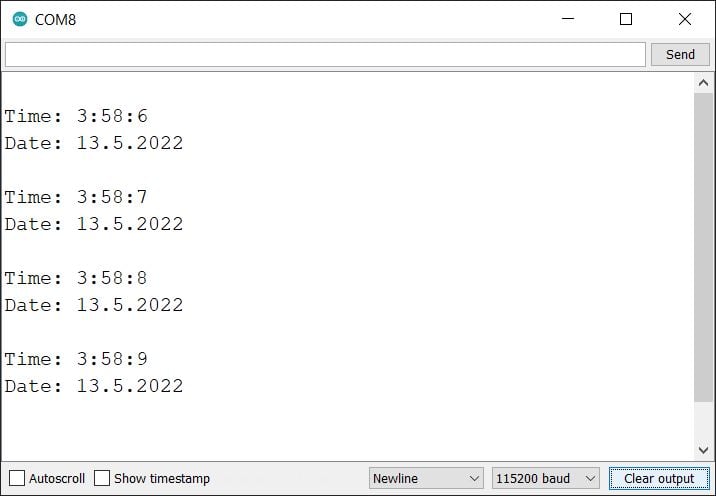
- After uploading the code open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 115200 then reset the ESP32 board
ESP32 serial output for DS1307 RTC
Let’s understand the code
First initialize the DS1307 Library.
#include <DS1307.h>Create the object as below
DS1307 rtc;Now with object “rtc”, we can access the functions from the “DS1307” class.
Then define the variables for the time and date.
uint8_t sec, minute, hour, day, month;
uint16_t year;
In setup function
We have initiated the serial communication with a 115200 Baud rate.
Now just begin the I2C communication and start the RTC communication
void setup(void){
Serial.begin(115200); /*Set the baudrate to 115200*/
rtc.begin();
rtc.start(); /*start RTC*/
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
}
In loop function
We will get the time and date using the following functions and print it on the serial monitor.
Here we will get,
- Time in Second, Minute, and Hour format
- Date in Day, Month, and Year format
void loop(void){
/*get time from RTC*/
rtc.get(&sec, &minute, &hour, &day, &month, &year);
/*serial output*/
Serial.print("\nTime: ");
Serial.print(hour, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minute, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(sec, DEC);
Serial.print("\nDate: ");
Serial.print(day, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(month, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(year, DEC);
Serial.println("");
/*wait a second*/
delay(1000);
}
Read the Time and Date using RTC DS1307 over ESP32 Web Server
ESP32 has oh-chip Wi-Fi, we can utilize it and monitor the readings over our smartphone, Laptop, or even smart TV.
We can use the ESP32 web server to monitor the time and date.
Now let’s take another example to display the same date and time on the web server using ESP32 and Arduino IDE.
Before uploading the code make sure you have added your SSID and Password as follows.
const char* ssid = "*Your SSID*"; /*Enter Your SSID*/
const char* password = "*Your Password*"; /*Enter Your Password*/Code for DS1307 RTC Web Server using ESP32
/*
ESP32 DS1307 RTC Web Server Code
http:://www.ElectronicWings.com
*/
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WebServer.h>
#include <DS1307.h>
#include "html.h"
WebServer server(80);
const char* ssid = "*Your SSID*"; /*Enter Your SSID*/
const char* password = "*Your Password*"; /*Enter Your Password*/
uint8_t sec, minute, hour, day, month;
uint16_t year;
DS1307 rtc;
void MainPage() {
String _html_page = html_page; /*Read The HTML Page*/
server.send(200, "text/html", _html_page); /*Send the code to the web server*/
}
void webRTC() {
String data = "[\""+String(hour)+"\",\""+String(minute)+"\",\""+String(sec)+"\",\""+String(day)+"\",\""+String(month)+"\",\""+String(year)+"\"]";
server.send(200, "text/plane", data);
}
void setup(void){
Serial.begin(115200); /*Set the baudrate to 115200*/
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); /*Set the WiFi in STA Mode*/
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
while(WiFi.waitForConnectResult() != WL_CONNECTED){Serial.print(".");} /*Wait while connecting to WiFi*/
Serial.print("Connected to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
Serial.print("Your Local IP address is: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); /*Print the Local IP*/
Serial.println("Init RTC...");
rtc.begin();
/*start RTC*/
rtc.start();
server.on("/", MainPage); /*Display the Web/HTML Page*/
server.on("/readwebRTC", webRTC); /*Display the updated Distance value(CM and INCH)*/
server.begin(); /*Start Server*/
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
}
void loop(void){
/*get time from RTC*/
rtc.get(&sec, &minute, &hour, &day, &month, &year);
/*serial output*/
Serial.print("\nTime: ");
Serial.print(hour, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minute, DEC);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(sec, DEC);
Serial.print("\nDate: ");
Serial.print(day, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(month, DEC);
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(year, DEC);
Serial.println("");
server.handleClient();
/*wait a second*/
delay(1000);
}
- Now upload the code. (while uploading the code make sure your ESP32 board is in the boot mode.)
- After uploading the code open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 115200 then reset the ESP32 board and check the IP address as shown in the below image
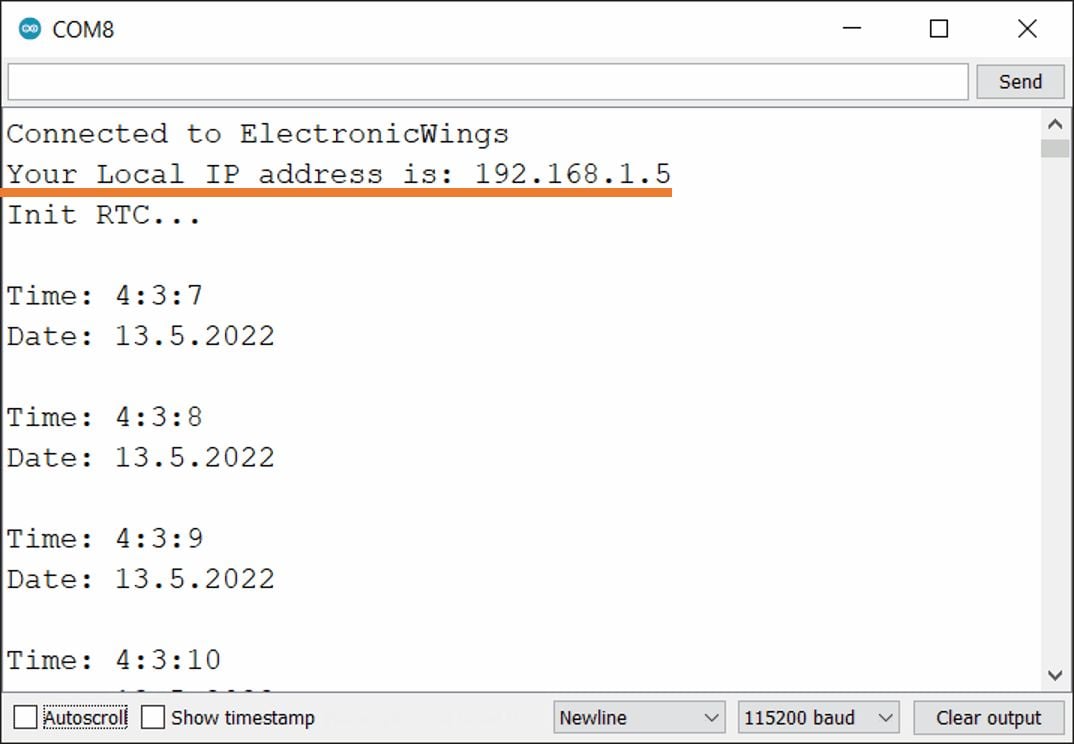
ESP32 Output on the webserver
- Now open any mobile or PC browser and type the IP address which is shown in the serial monitor and hit the enter button.
- If all are ok, then the web page will start the showing current time and date on the web server like in the below image.
Note: make sure your ESP32 and mobile are connected to the same router/server, if they are connected to the same router or server then only you will be able to visible the web page.
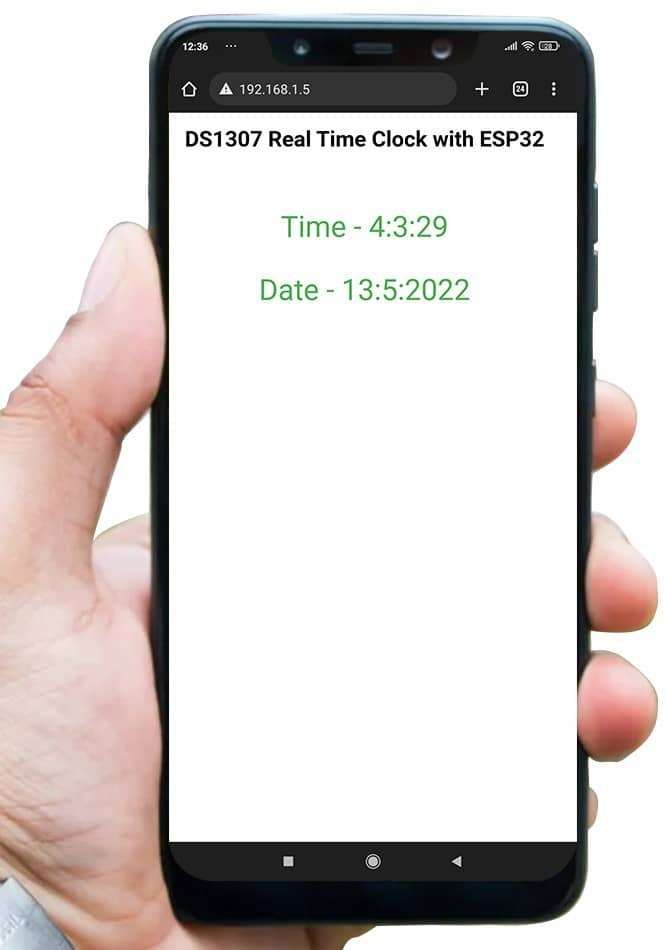
Let’s Understand the code
To understand this code, please refer to the basics guide of “How to create the ESP32 Server”.
Once you get the basics of ESP32 server creation, it will be very simple to understand the code.
This code starts with important header files and libraries, In WiFi.h file contains all ESP32 WiFi related definitions, here we have used them for network connection purposes.
The WebServer.h file supports handling the HTTP GET and POST requests as well as setting up a server. In the html.h file contains all the web page code and then add the DS1307 library file.
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WebServer.h>
#include "html.h"
#include <DS1307.h>Let’s define HTTP port i.e., Port 80 as follows
WebServer server(80);Declare a variable of type uint8_t and uint16_t
uint8_t sec, minute, hour, day, month;
uint16_t year;Create an rtc object of DS1307
DS1307 rtc;
Setup Function
In the setup function, first we set the WiFi as an STA mode and connect to the given SSID and password
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); /*Set the WiFi in STA Mode*/
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
delay(1000); /*Wait for 1000mS*/
while(WiFi.waitForConnectResult() != WL_CONNECTED){Serial.print(".");}After successfully connecting to the server print the local IP address on the serial window.
Serial.print("Your Local IP address is: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); /*Print the Local IP*/
Handling Client Requests and Serving the Page:
To handle the client request, we use server.on() function.
It takes two parameters, The first is requested URL path, and the second is the function name, which we want to execute.
As per the below code, when a client requests the root (/) path, the “MainPage()” function executes.
Also, when a client requests the “/readwebRTC” path, The webRTC() function will be called.
server.on("/", MainPage); /*Client request handling: calls the function to serve HTML page */
server.on("/readwebRTC", webRTC); /*Display the updated Distance value(CM and INCH)*/Now start the server using server.begin() function.
server.begin(); /*Start Server*/
Functions for Serving HTML
We have defined the complete HTML page in a file named “html.h” and added it to the header file. With the following function, we are sending the complete page to the client via server.send() function.
While sending, we are passing the first parameter “200” which is the status response code as OK (Standard response for successful HTTP requests).
Second parameter is the content type as “text/html“, and the third parameter is html page code.
void MainPage() {
String _html_page = html_page; /*Read The HTML Page*/
server.send(200, "text/html", _html_page); /*Send HTM page to Client*/
}Now in the below function only we are sending the updated time and calendar values to the web page.
void webRTC() {
String data = "[\""+String(hour)+"\",\""+String(minute)+"\",\""+String(sec)+"\",\""+String(day)+"\",\""+String(month)+"\",\""+String(year)+"\"]";
server.send(200, "text/plane", data);
}
Loop Function
Now to handle the incoming client requests and serve the relevant HTML page, we can use handleClient() function. It executing relevant server.on() as a callback function although it is defined in void setup()
So, it continuously serves the client requests.
server.handleClient();
HTML Page Code
/*
ESP32 DS1307 HTML Web Page Code
http:://www.electronicwings.com
*/
const char html_page[] PROGMEM = R"RawString(
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
body {font-family: sans-serif;}
h1 {text-align: center; font-size: 30px;}
p {text-align: center; color: #4CAF50; font-size: 40px;}
</style>
<body>
<h1>DS1307 Real Time Clock with ESP32 </h1><br>
<p>Time - <span id="_HOUR">0</span>:<span id="_MIN">0</span>:<span id="_SEC">0</span></p>
<p>Date - <span id="_DAY">0</span>:<span id="_MONTH">0</span>:<span id="_YEAR">0</span></p>
<script>
setInterval(function() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
const text = this.responseText;
const myArr = JSON.parse(text);
document.getElementById("_HOUR").innerHTML = myArr[0];
document.getElementById("_MIN").innerHTML = myArr[1];
document.getElementById("_SEC").innerHTML = myArr[2];
document.getElementById("_DAY").innerHTML = myArr[3];
document.getElementById("_MONTH").innerHTML = myArr[4];
document.getElementById("_YEAR").innerHTML = myArr[5];
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "readwebRTC", true);
xhttp.send();
},100);
</script>
</body>
</html>
)RawString";
Let’s understand the code step by step
All html pages start with the <!DOCTYPE html> declaration, it is just information to the browser about what type of document is expected.
<!DOCTYPE html>The html tag is the container of the complete html page which represents on the top of the html code.
<html>
Now here we are defining the style information for a web page using the <style> tag. Inside the style tag we have defined the font name, size, color, and test alignment.
<style>
body {font-family: sans-serif;}
h1 {text-align: center; font-size: 30px;}
p {text-align: center; color: #4CAF50; font-size: 40px;}
</style>Inside the body, we are defining the document body, in below we have used headings, and paragraphs if you want you can add images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc. also.
On the web page, we are displaying the heading of the page, and inside a paragraph Time and Calendar values.
Now Time and Date values updates under the span id which is manipulated with JavaScript using the id attribute.
<h1>DS1307 Real Time Clock with ESP32 </h1><br>
<p>Time - <span id="_HOUR">0</span>:<span id="_MIN">0</span>:<span id="_SEC">0</span></p>
<p>Date - <span id="_DAY">0</span>:<span id="_MONTH">0</span>:<span id="_YEAR">0</span></p>
Now, this is the javascript that comes under the <script> tag, this is also called a client-side script.
<script>In setInterval() method we are calling the function at every 50mS intervals.
setInterval(function() {},50);here we are creating the html XMLHttpRequest object
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
The xhttp.onreadystatechange event is triggered every time the readyState changes and the readyState holds the status of the XMLHttpRequest.
Now in the below code, the ready state is 4 means the request finished and response is ready and the status is 200 which means OK.
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
const myArr = JSON.parse(this.responseText);Now here is the main thing, we are updating the clock and calendar values in html page using _ HOUR, _ MIN, _SEC,_ DAY, _MONTH, and _YEAR id.
document.getElementById("_HOUR").innerHTML = myArr[0];
document.getElementById("_MIN").innerHTML = myArr[1];
document.getElementById("_SEC").innerHTML = myArr[2];
document.getElementById("_DAY").innerHTML = myArr[3];
document.getElementById("_MONTH").innerHTML = myArr[4];
document.getElementById("_YEAR").innerHTML = myArr[5];
Here we used the AJAX method to send the updated values to the server without refreshing the page.
In the below function we have used the GET method and sent the readwebRTC function which we defined in the main code asynchronously.
xhttp.open("GET", "readwebRTC", true);Send the request to the server using xhttp.send(); function.
xhttp.send();
Close the script
</script>Close the body
</body>Close the html.
</html>
Components Used |
||
|---|---|---|
| DS1307 RTC DS1307 RTC DS1307 RTC DS1307 RTC |
X 1 | |
| ESP32 WROOM WiFi Development Tools - 802.11 ESP32 General Development Kit, embeds ESP32-WROOM-32E, 4MB flash. |
X 1 | |